“Volatility Storms: Understanding Cryptocurrency Price Volatility and Polygon (POL) Periods”
In the ever-evolving world of cryptocurrencies, one of the most significant challenges investors and traders face is price volatility. This phenomenon refers to the rapid and unpredictable fluctuations in the value of cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin (BTC) or Ethereum (ETH), resulting in significant gains and losses for the parties involved. Two key factors that contribute to these volatility storms are
wrestling periods
, the decision-making period, and the inherent uncertainty surrounding blockchain technology.
Wrestling Period: The Vital Period
A wrestling period refers to a time when the value of a cryptocurrency has dropped significantly, causing investors to reassess their positions. This is especially common for cryptocurrencies that have experienced price declines due to factors such as market speculation, regulatory issues, or increased competition from new players entering the market.
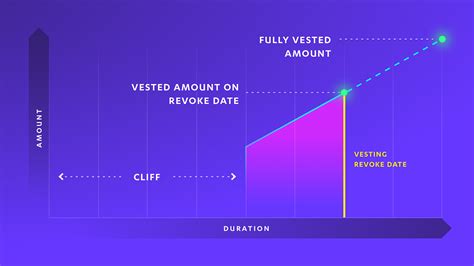
During this period,
vesting periods apply, which are predetermined time intervals during which the holder of a particular cryptocurrency can sell it at the current market price. These vesting periods can range from 5 to 30 weeks depending on the specific cryptocurrency and its underlying blockchain technology (e.g., Ethereum smart contract-based system). The duration and structure of these vesting periods are critical in determining how much risk investors are willing to take.
Polygon: A Blockchain-Optimized Solution
Polygon is a Layer 2 scaling solution designed for the Ethereum network that aims to improve its scalability by offloading some of the computing power from miners. Polygon (POL) is built on the Ethereum blockchain and uses a unique consensus algorithm called Proof of Stake (PoS). This allows for faster transaction times, lower fees, and greater energy efficiency.
Polygon Utility Token: Polygon (POL)
One of the most notable aspects of Polygon is its native token, Polygon (POL). POL can be used to pay for transactions on the Polygon network, as well as to participate in the staking process. Staking POL allows holders to earn interest on their investment and support the growth of the network.
To become a holder or investor in Polygon, you must purchase POL tokens through various exchanges or marketplaces. These funds are then locked up for a period of time during which they cannot be sold until the own portion of the investment reaches 70% of its total value.
Conclusion
Cryptocurrency price volatility and grace periods are a major concern for investors and traders in the cryptocurrency world. Understanding these factors is key when making informed decisions about when to buy, sell, or hold cryptocurrencies like Polygon (POL). By understanding the struggle period, vesting period, and native utility tokens associated with Polygon, you can better navigate the complexities of this rapidly evolving market.
Disclaimer:
This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered investment advice. Trading in cryptocurrencies carries significant risks, including market fluctuations, regulatory issues, and security concerns. Always do your own research, set a budget, and never invest more than you can afford to lose.
